NMDA receptor antagonist | BIII 277CL
Highlights
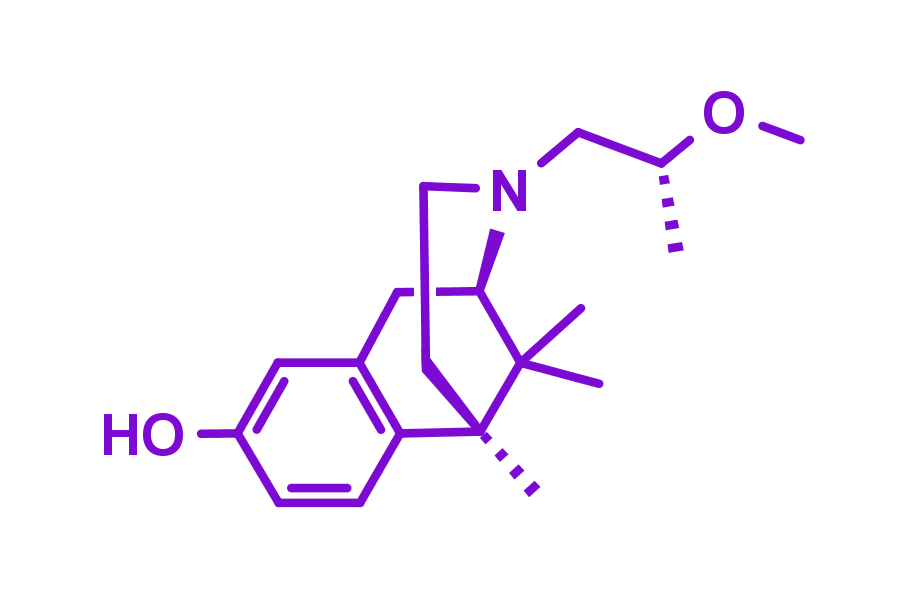
BIII 277CL is a selective high affinity blocker of the NMDA receptor ion channel (Ki = 4.5 nM). This molecule is available for both in vitro and in vivo experiments. In mice, it showed significant neuroprotective effects. BIII 277CL showed dose-dependent reduction of the cortical infarct area in mice with focal cerebral ischemia and also prevented NMDA-induced lethality.
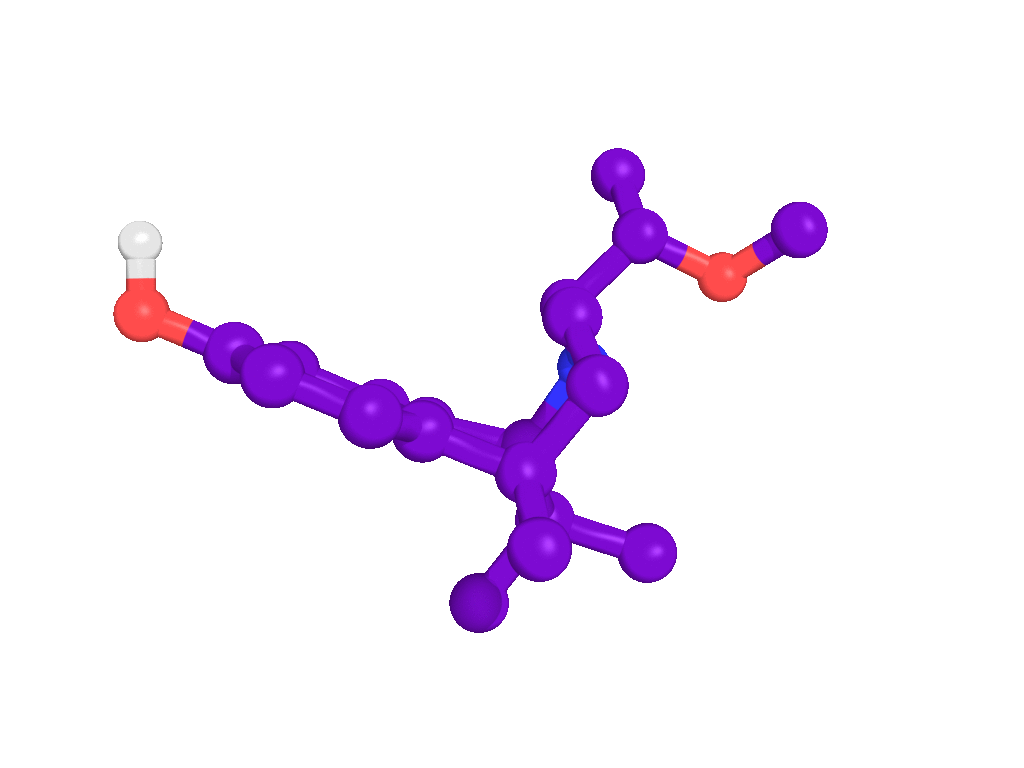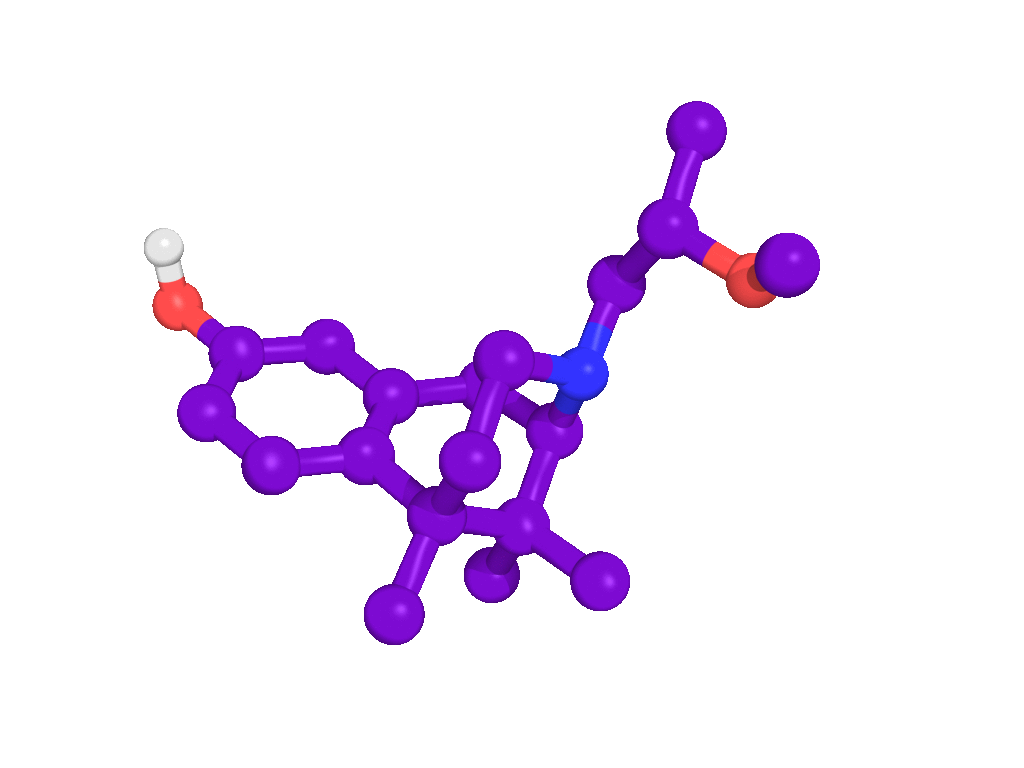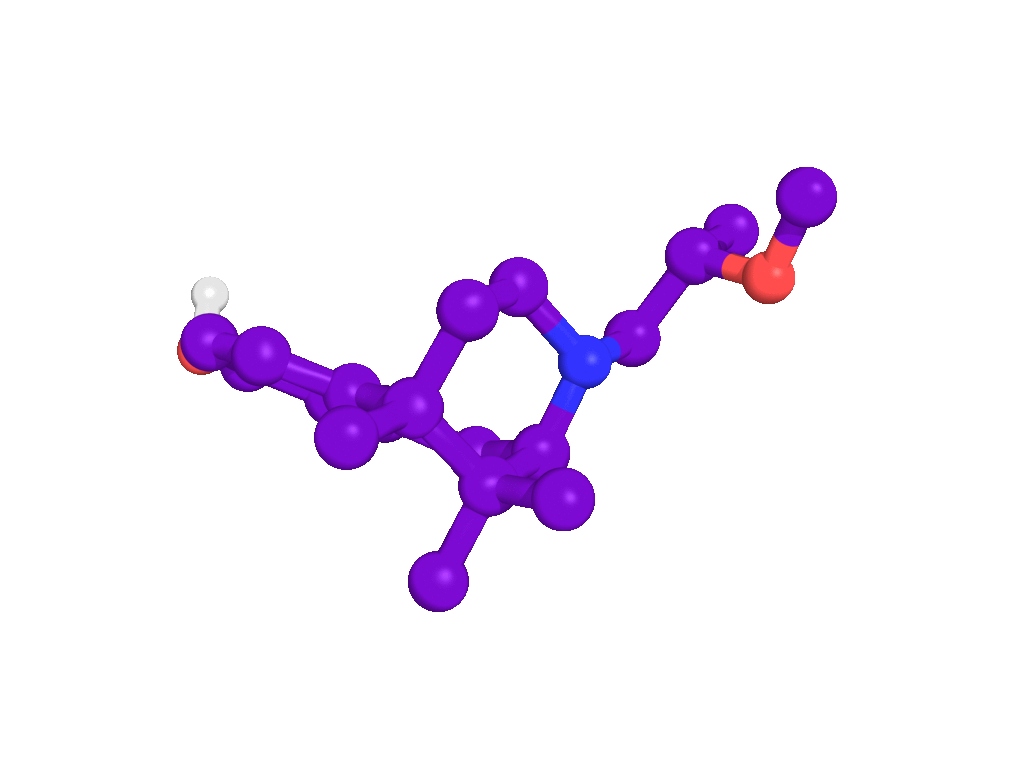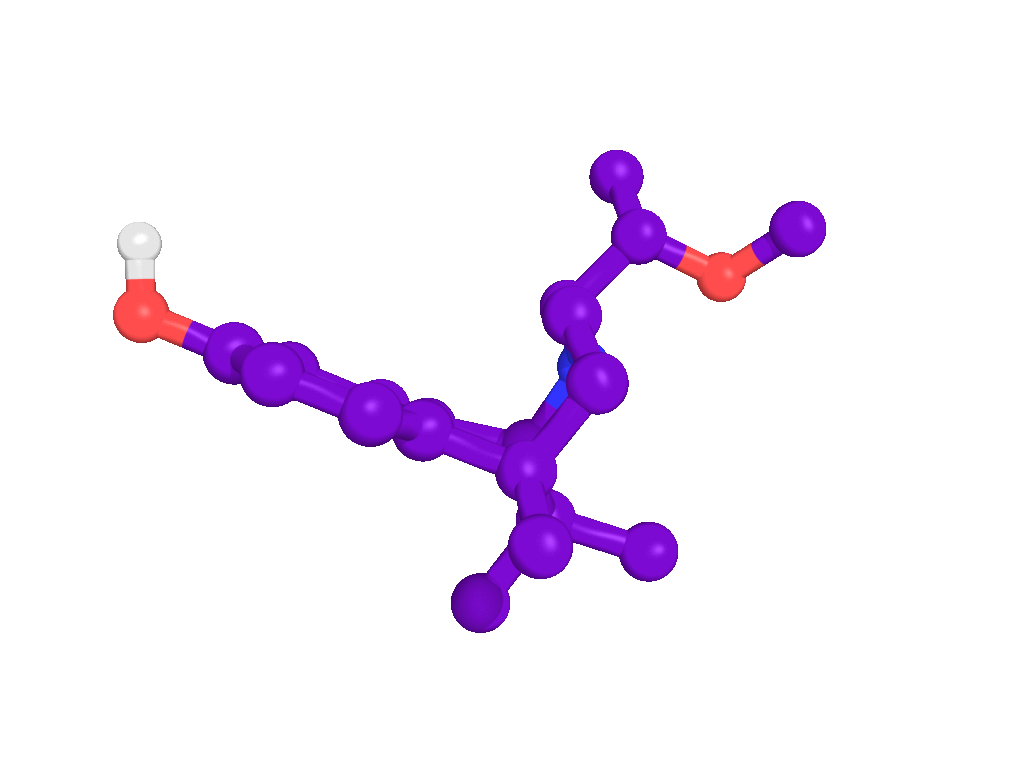
Background information
Target Information
The NMDA receptor is a subtype of excitatory amino acid receptor found in nerve cells, which allows cationic influx upon activation by glutamate and glycine.
Structurally, the NMDA receptor–channel complex consists of a voltage-dependent Na+/Ca2+ channel and at least 3 different regulatory domains: neurotransmitter recognition site (glutamate, aspartate, or NMDA binding site), strychnine-insensitive glycine site, and ion channel itself (can be blocked by Mg2+ or other blockers).
During ischemia, large amounts of glutamate and aspartate (excitatory neurotransmitters) are released into the extracellular space, which can lead to neuronal deaths. This implicates the NMDA receptor–channel complex with pathophysiology of numerous neurological disorders, such as stroke, epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, ALS, and others.
BIII 277CL is a high affinity blocker of the NMDA receptor ion channel with specificity over other binding sites of the NMDA receptor–channel complex. In addition, BIII 277CL did not exhibit significant affinities for other central neurotransmitter receptors.
BIII 277CL also antagonized NMDA-induced [3H]noradrenaline release and NMDA-induced inhibition of protein synthesis in rat hippocampal slices.
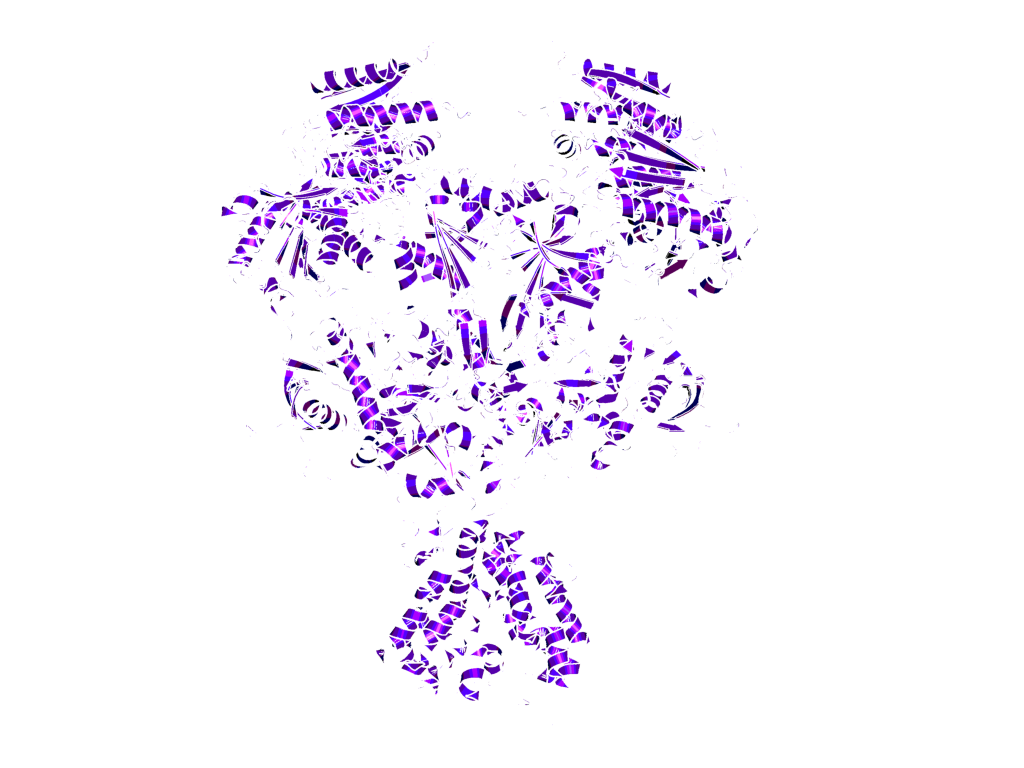
Structure of the NMDA receptor from Xenopus laevis (4TLM.pdb; Lee et. al., Nature 511 (2014), p.191-197)
In vitro activity
BIII 277CL is a high affinity blocker of the NMDA receptor ion channel (Ki = 4.5 nM; [3H]MK-801 displacement assay in rat brain synaptosomal membrane) with specificity over other binding sites of the NMDA receptor–channel complex (glycine and NMDA binding sites). In addition, BIII 277CL did not exhibit significant affinities for other central neurotransmitter receptors.
Probe name / negative control | BIII 277CL | BI-25CL |
| MW [Da] | 339.1 (HCl Salt) | 339.1 (HCl Salt) |
Displacement of [3H]MK-801 Ki [nM]a MK-801: dizocilpine | 4.5 | >50,000 |
a Assay conditions see reference 1
In vitro DMPK and CMC parameters
Probe name / negative control | BIII 277CL | BI-25CL |
| Solubility @ pH 7 [µg/ml] | >38 | >74 |
| Solubility @ pH 4 [µg/ml] | 53.7 | >77 |
| CACO permeability @ pH 7.4 [*10-6 cm/s] | ongoing | ongoing |
| CACO efflux ratio | ongoing | ongoing |
| MDCK permeability Pappa-b/b-a @ 1µM [10-6 cm/s] | ongoing | ongoing |
| MDCK efflux ratio | ongoing | ongoing |
| Microsomal stability (human) [% QH] | 49 | ongoing |
| Hepatocyte stability (human/mouse/rat) [% QH] | ongoing | ongoing |
| Plasma protein binding (human/mouse/rat) [%] | ongoing | ongoing |
| CYP 3A4 (IC50) [µM] | >50 | >50 |
| CYP 2C8 (IC50) [µM] | >50 | >50 |
| CYP 2C9 (IC50) [µM] | >50 | >50 |
| CYP 2C19 (IC50) [µM] | >50 | 18.5 |
| CYP 2D6 (IC50) [µM] | 14.7 | >50 |
In vivo DMPK parameters
BIII 277CL | RAT |
| Clearance [% QH]b | ongoing |
| tmax [h] | 0.3 |
| Cmax [nM]a | 2.691 |
| F [%] | 4.301 |
| Vss [l/kg] | >100.000 |
b dose [mg/kg]
In vivo pharmacology
In mice, BIII 277CL showed significant neuroprotective effects. The title compound prevented NMDA-induced lethality and caused disturbances in motor coordination (ID50 = 0.54 mg/kg s.c. and ED50 = 0.47 mg/kg s.c., respectively).
Furthermore, intraperitoneal or subcutaneous application of BIII 277CL to mice dose-dependently reduced the cortical infarct area from focal cerebral ischemia by unilateral occlusion of the middle cerebral artery.
Negative control
In addition, we offer a structurally closely related BI-25CL, which showed no marked affinity at the NMDA receptor ion channel (Ki = 50 μM; [3H] MK-801 displacement assay in rat brain synaptosomal membrane) to be used as a control compound in in vitro studies.

BI-25CL which serves as a negative control
Selectivity
BIII 277CL displayed only weak affinities for σ- and μ-opiate binding sites ([3H]DTG, [3H]dihydromorphine, [3H]naloxone displacement assays in rat brain synaptosomal membrane) and 200-fold selectivity toward the channel site of the NMDA receptor–channel complex with no marked affinities up to 10 μM for the glycine site and the NMDA binding site of the NMDA receptor–channel complex.
Additionally, BIII 277CL did not exhibit affinities up to 100 μM for the dopamine D1 and D2 receptors ([3H]SCH 23390 and [3H]spiroperidol displacement assay).
| SELECTIVITY DATA AVILABLE | BIII 277CL | BI-25CL |
SafetyScreen44™ with kind support of  | Yes | Yes |
| Invitrogen® | No | No |
| DiscoverX® | No | No |
| Dundee | No | No |
Download selectivity data:
BIII-277CL_selectivityData_0.xlsx
BI-25CL_selectivityData.xlsx
Reference molecule(s)
For an overview of NMDA receptor antagonists please refer to the corresponding Wikipedia article and references therein.
Summary
BIII 277CL is a highly potent and selective antagonist of the NMDA receptor (Ki 4.5 nM) that can be used to test biological hypotheses.
Supplementary data
2 D structure formats available
NMDA channel blocker | BIII 277CL.png
NMDA channel blocker | BIII 277CL.smiles
NMDA channel blocker | BIII 277CL.sdf
Negative control | BI-25CL.png
References
How to cite opnMe?
When you plan a publication, please use the following acknowledgement:
BIII 277CL was kindly provided by Boehringer Ingelheim via its open innovation platform opnMe, available at https://opnme.com.






